|
The main question when creating artificial intelligence is how the learning process takes place.
1 way:
Modern attempts to create AI are based primarily on neural networks,
and, it must be acknowledged that these attempts are rather effective and have borne fruit in a number of industries:
1)Unmanned cars (companies Tesla и Google)

2)Pattern recognition (Google images)

3)Speech recognition (Siri, OK Google)

4)Universal translator (Google translator)

But the approach to creating AI based on neural networks has a number of limitations stemming from the very meaning of neural networks. What are neural networks?
This is a huge set of small signal transmitters - neurons (in the human brain up to 100 billion pieces) interacting with each other. These transmitters can receive and send signals in accordance with a certain behavior program.
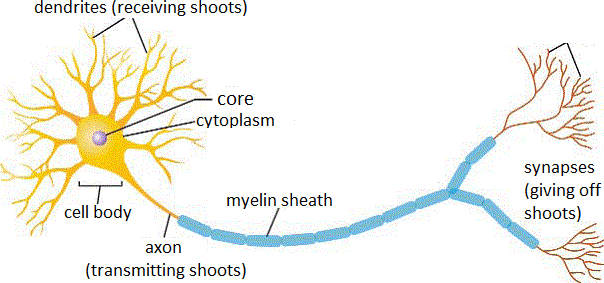
There are different models and different programs, but in essence the work of neural networks can be described as follows: imagine a person to whom important information was transmitted - this person got excited, started to try to find to whom can be transfered this important information and distribute the information as much as possible Wider. And so he began to run up to everyone on the street in an attempt to tell his knowledge. But someone is very busy and can not answer, someone can, but does not understand the person seeking communication. Someone can and understands - but just do not know what to do next with this information and turns out to be a dead-end addressee. And only a few will be able to receive the signal, understand the signal and broadcast it further. Neurons also behave the same way. After receiving the signal, they randomly communicate to all the other neurons in an attempt to spread the signal further. So chains of neural connections are built-chains of those neurons that could interact.

The key problem is that a random walk of the signal in search of the addressee can last too long (millions of years) or may not be successful at all (in view of the death of the neuron or switching it to other tasks).

ie once again - learning based only on neural networks is too long a path and an unreliable path because by chance.

Therefore, there are other ways:
2 way: repetition
Thus, children are taught in schools in 90% of cases. Multiple repetition of a preconceived program leads to its assimilation. But there is no so-called creative element.
Reason, brought up on repetition, gets used to it and becomes incapable of independent learning through neural networks - a long, but effective way. And just as incapable of analyzing and structuring information - to the 3-rd way, which the Pangeya technology pave to create the AI

3 way: analysis of information structure
THINKING IS A COMPARISION! - here it is the key idea of the whole technology Pangeya: comparison of blocks of information through analysis of the structure of this information!

To create the idea, to the signal between neurons has passed - it is necessary to note the similarity of one block of information to another!
ie imagine again a man running along the street in an attempt to convey a thought - but speaking a foreign language with everyone on the street - he can not do it! He is just no one will understand! But if a person speaks one language with you or at least looks like a SIMILAR language, then you already have chances to understand each other.

So it is with artificial intelligence. He takes into consideration two blocks of information: and if he finds them in something similar - creates a link. If they are completely different, it compares other blocks of information until a link is found.
And the structure of information can be described through objects endowed with properties. And it is through the comparison of properties that we can compare objects with each other and establish their similarities.
People never come up anything, and it's impossible at all. You can observe the surrounding reality, and compare the previously stored information with information coming from outside. If we find a strong similarity of what is available and come - an idea is born = a link. And we always inevitably make a comparison by analyzing the properties of objects
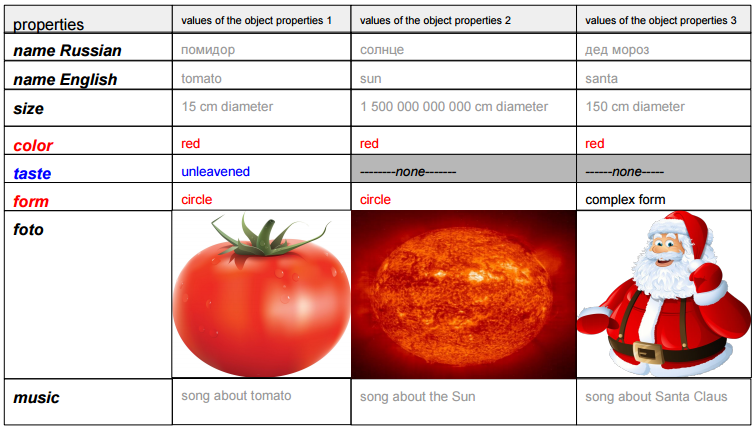
So, for example, from the table above you can see that Tomato and the Sun are more similar to each other (by the properties of the form and color) than the grandfather Frost and the tomato (by the properties of the color).
In conclusion, I must say that all three of the above-mentioned methods of learning are important and necessary. And they should be used all 3-only so you can achieve effective result.
Neural networks are good - when you are learning something completely new, generally unknown. But this is long and unreliable.
Repetition and ready algorithms are good - where the articficial intellegence should be taught very quickly and accurately to something already known in advance.
And the analysis of the structure of information is simply vital, when it is necessary to create new information on the basis of what was previously studied through the formation of links = similarities based on the analysis of the properties of objects. This is the so-called logical thinking.

Essentially, all 3 ways are manifestations of different aspects of the same process:
1)repetition: people contribute to their accounts the information they know, i.e. as a matter of fact repeat that already know to the computer

2)the information entered will randomly be compared in its structure with other information described in the same properties - neural networks operate here, they will carry out a search process with whom to interact

3)and finally, at the tip of the pen - at the moment of contact of 2 blocks of information selected by the neural network, objects will be compared through their properties

|